Review flagged transactions
After GL Outlier Detection is configured and running, transactions submitted to a journal for approval go through GL Outlier Detection for evaluation.
| Subscription |
AI/Machine Learning General Ledger |
|---|---|
| Regional availability |
All regions |
| User type | Business user with admin privileges |
| Permissions | Journal entries: View, List, Approve, Add, Edit |
| Prerequisites | GL Outlier Detection configured and indexed. Optionally, Outlier Assistant is enabled. |
The evaluation process runs in the background and Approvers can see the Outlier status in the List view.
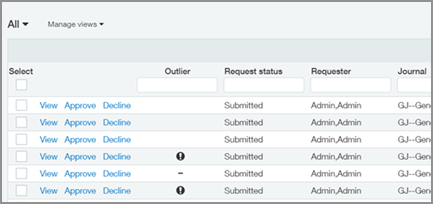
List-level icons
The Outlier column shows the state of Outlier detection:
- Empty ( ): The transaction has not been evaluated yet, even though it’s been submitted. Evaluation can take a while after submission.
- An exclamation mark (Outlier exclamation): At least one line entry in the transaction is an outlier.
- A dash (Nonoutlier dash): No outliers have been detected in the transaction based on your historical data and the model.
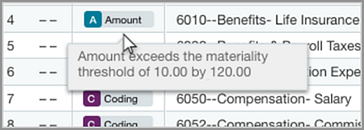
Line-level icons
Indicator icons on individual transaction lines let you see whether an outlier is flagged as a coding anomaly, an amount anomaly, or multiple anomalies. This makes it easier to pinpoint which item to look for in the submission.
When reviewing the transaction details, you’ll see an indication of why the line has been flagged as an outlier. Moving your mouse over the icon provides even more information. Icons include:
-
 Coding outlier: the account-dimension, dimension-dimension, or account-journal relationship is an outlier.
Coding outlier: the account-dimension, dimension-dimension, or account-journal relationship is an outlier. -
 Amount outlier: the amount-journal relationship is an outlier.
Amount outlier: the amount-journal relationship is an outlier. -
 Multiple outliers: there are at least 2 types of outliers.
Multiple outliers: there are at least 2 types of outliers.
What to look for when a transaction is flagged
Outlier detection flags irregular amounts and unusual combinations of the following dimensions:
-
Account
-
Department
-
Location
-
Vendor
-
Class
-
Project (if subscribed to Projects)
When you see that a transaction has an outlier, open the transaction details. If a transaction contains an outlier:
- A notification appears at the top of a transaction.
- The Outlier column in the entries table indicates the outlier entry.
To see details about an outlier, hover over Outlier.
The next step is yours
GL Outlier Detection provides an additional data point as you complete the approval decision. You still have the option to approve, manually correct, or decline the transaction.
The action you take on the transaction is included when the data model is refined. This information enables ongoing improvement to the data model.
GL Outlier Detection is a helpful tool when approving entries, but it is not a substitute decision maker. No tool—not even AI—is foolproof. The ultimate decision on which action to take is yours.
If you’re using Outlier Assistant
If Outlier Assistant is enabled, entries flagged as outliers are sent back to the submitter before being passed to the Approver.
In this case, the submitter initially determines if changes are needed to the entry, or they can send it to the Approver as is.
After the submitter updates the entry or determines that it is correct, it is sent on to the Approver as usual.
How does GL Outlier Detection flag entries?
GL Outlier Detection uses your historical data to identify patterns in your General Ledger journal entries. It flags incoming entries that do not conform to those patterns. Patterns are typically established on a per-journal basis and largely based on standard fields of an entry, such as account, key dimensions, and amount.
GL Outlier Detection is dynamic, meaning it continually learns as new data becomes available and new patterns emerge. For example, a transaction is flagged at first, but then a new pattern is recognized. Entries conforming to the newly identified pattern are no longer flagged as outliers.
What does it mean when an entry is flagged?
If a General Ledger journal entry is flagged as an outlier, the algorithm has determined that the entry is unusual based on the available data and the currently identified patterns. The reason that the entry is flagged can be viewed by hovering over the outlier flag within the entry. The reason it's flagged could be:
- It uses a value for a dimension that’s not typically used in this journal.
- It uses a new type of entry that’s never been seen in the data before.
- It does not conform to other patterns identified by the algorithm.
GL Outlier Detection algorithms are based on common transaction practices and consider relationship patterns in historical data. In some cases, your business practices can evolve or be different for a legitimate reason that GL Outlier Detection has not identified as a pattern. Consequently, GL Outlier Detection flags some entries that you consider normal. The flag is an additional tool to guide you to transactions that require extra scrutiny.
What does it mean when an entry is not flagged?
There could be many reasons why an entry is not flagged or needs extra attention. This can be due to a policy change within your business, for example, or another type of issue that the algorithm has not yet detected.
GL Outlier Detection is another data point in your review process, which can help when you review journal entries, flagged and unflagged, for approval.
